Solar Panel ROI Explanation
What is ROI in the context of Solar Panels?
ROI, or Return on Investment, is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. In solar panels, ROI measures the economic return on your investment in solar energy over a specific period, usually the solar system’s lifespan. It is expressed as a percentage and helps determine whether the investment is financially worthwhile.
Why is calculating ROI essential for potential solar panel buyers?
Calculating ROI is crucial for buyers of solar panels. You can calculate ROI by using our tool. It clearly explains the financial benefits of installing solar panels, helping homeowners make informed decisions. Understanding the costs and savings associated with solar panels is key to effective budgeting. ROI demonstrates how solar panels benefit the environment and save money, making the decision to use renewable energy more appealing.
Few benefits of a high ROI
A high ROI indicates that the investment in solar panels is yielding significant financial benefits. This can save a lot on electricity bills, lower utility costs, and raise disposable income. A higher ROI usually means a shorter payback period, so the savings cover the initial investment faster. Homes with solar panels often increase in value. While solar panels can also increase the value of your home. Buyers prefer energy-efficient homes. A high ROI means big profits. It also shows a positive impact on the environment. It reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers carbon emissions.
Key Factors Influencing Solar Panel ROI
Several factors influence the ROI of solar panels. The upfront cost of purchasing and installing the solar system is a significant factor; lower initial costs lead to a higher ROI. Solar energy cuts electricity bills, improving ROI. Incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, can significantly lower the initial investment, thereby boosting ROI. Ongoing costs for maintenance and operation can affect the overall savings and ROI. The efficiency and lifespan of the solar panels determine how long they will generate savings. Finally, sunlight affects energy production and savings, impacting ROI.
6 Steps to Calculate Solar Panel ROI
Step 1: Determine Initial Costs
To calculate the ROI of your solar panel investment, start by determining the initial costs. This includes:
- Equipment Costs: The price of solar panels, inverters, batteries (if applicable), and other hardware.
- Installation Costs: Labor costs for installing the solar system, which can vary depending on the complexity of the installation.
- Permits and Inspection Fees: Local government fees for permits and inspections required for the installation.
- Additional Expenses: Costs for mounting systems, wiring, and any necessary upgrades to your system.
For example, if you’re installing a 10kW solar system, the breakdown might look like this:
- Equipment: $15,000
- Installation: $5,000
- Permits and Fees: $1,000
- Additional Expenses: $1,000
- Total Initial Costs: $22,000
Step 2: Calculate Annual Energy Savings
Next, estimate the annual energy savings you’ll achieve with your solar panels. This involves:
- Current Electricity Usage: Review your electricity bills to determine your average annual electricity consumption.
- Solar Panel Output: Calculate the expected energy production of your solar panels based on their efficiency and your location’s average sunlight hours.
For instance, if your household consumes 10,000 kWh per year and your 10kW solar system produces 12,000 kWh per year, you can offset your entire electricity usage. Assuming an average electricity rate of $0.13 per kWh, your annual savings would be:
Annual Energy Savings: 10,000 kWh * $0.13/kWh = $1,300
Step 3: Factor in Incentives and Rebates
Federal and state incentives can significantly reduce the initial costs of your solar installation. These might include:
- Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC): This credit currently offers a 26% reduction on your total solar system costs.
- State and Local Rebates: Many states and municipalities offer additional rebates and incentives.
Using the previous example:
- Federal ITC: 26% of $22,000 = $5,720
- Net Initial Costs: $22,000 – $5,720 = $16,280
Step 4: Estimate Maintenance and Operating Costs
While solar panels require minimal maintenance, you should account for:
- Cleaning Costs: Periodic cleaning to remove dust and debris.
- Inverter Replacement: Inverters may need replacement after 10-15 years.
- Monitoring System: If you choose to use a monitoring service to track your system’s performance.
Assume an average annual maintenance cost of $200:
- Total Maintenance Costs Over 25 Years: $200 * 25 = $5,000
Step 5: Calculate the Total Savings Over the System’s Lifespan
Sum up the total savings you’ll achieve over the solar system’s lifespan, typically 25-30 years. Include both the annual energy savings and any additional savings from incentives.
Using our example:
- Annual Energy Savings: $1,300
- Total Savings Over 25 Years: $1,300 * 25 = $32,500
Step 6: Compute the ROI
Finally, calculate the ROI using the following formula:
ROI= (Net Initial CostsTotal Savings ÷ Net Initial Costs) ×100
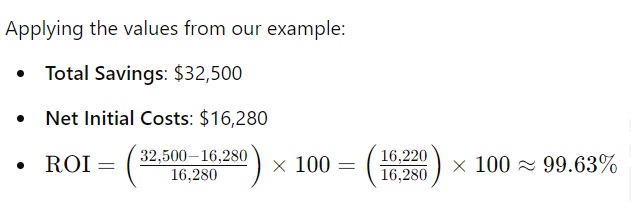
This means that over 25 years, your solar panel investment would yield an ROI of approximately 99.63%.
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the ROI of your solar panel investment, helping you make an informed decision about the financial benefits of going solar.